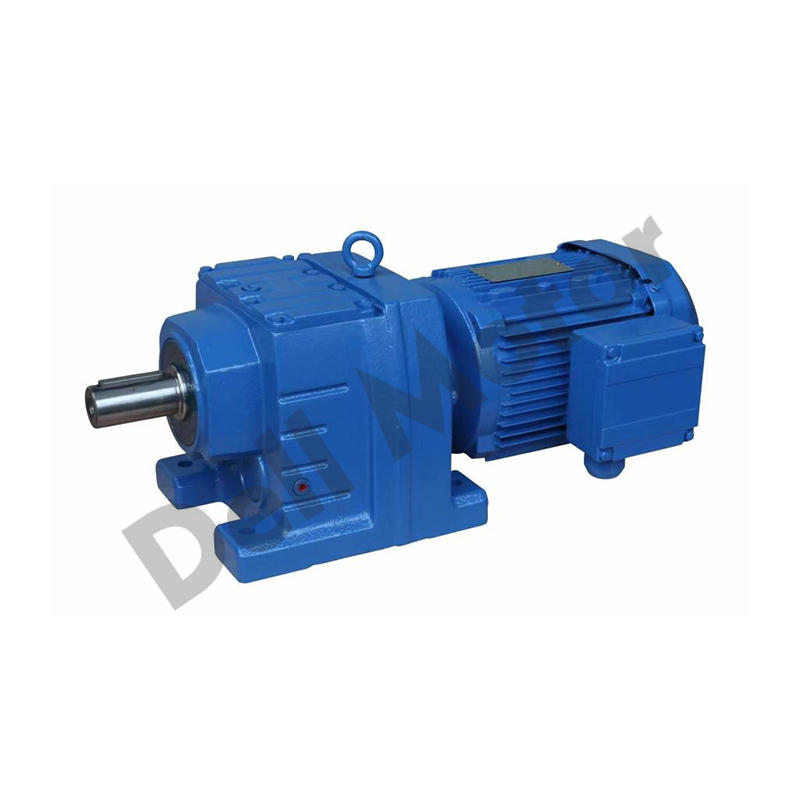
Electric gear motors are an indispensable component in numerous industrial, commercial, and residential applications, serving to efficiently convert electrical energy into mechanical motion.
Fundamental Principles
At their core, electric gear motors consist of an electric motor coupled with a gear train. The electric motor, typically an AC or DC motor, generates rotational motion when electrical current flows through its coils, creating a magnetic field that interacts with the motor's permanent magnets or electromagnets. This rotational motion is then transmitted to the gear train.
The gear train, composed of multiple gears of different sizes, serves to modify the motor's output speed and torque. By meshing gears with varying numbers of teeth, gear motors can amplify torque while reducing rotational speed (gear reduction) or increase speed while reducing torque (gear increase). This ability to trade speed for torque or vice versa makes gear motors highly versatile and suitable for a wide range of applications.
Applications
Electric gear motors find application in diverse industries and settings:
Industrial Automation: In manufacturing processes, gear motors drive conveyor belts, robotic arms, and other automated equipment. Their precise control and ability to maintain consistent torque facilitate smooth and efficient operation.
Automotive: Electric gear motors power various components in vehicles, including windshield wipers, power windows, and seat adjusters. In electric and hybrid vehicles, gear motors are integral to the propulsion system, controlling the speed and torque of the wheels.
HVAC Systems: Heating, ventilation, and air conditioning (HVAC) systems utilize gear motors to drive fans, dampers, and valves, regulating airflow and temperature in commercial and residential buildings.
Medical Devices: Gear motors are employed in medical equipment such as infusion pumps, diagnostic devices, and surgical instruments, where precise motion control is essential for patient safety and treatment efficacy.
Home Appliances: From kitchen appliances like blenders and food processors to garage door openers and electric lawnmowers, gear motors play a crucial role in enhancing the functionality and efficiency of household devices.
Renewable Energy: Wind turbines and solar tracking systems utilize gear motors to adjust blade pitch and solar panel orientation, optimizing energy capture and maximizing output.
Agricultural Machinery: Tractors, harvesters, and irrigation systems rely on gear motors to power various functions, such as steering, seeding, and lifting heavy loads.
Benefits
Electric gear motors offer several advantages over other types of motive power:
High Efficiency: Gear trains help improve efficiency by transmitting power with minimal losses, reducing energy consumption and operational costs.
Compact Design: By compactly integrating the motor and gearbox, gear motors occupy less space compared to systems employing separate motors and external gearing.
Precise Control: Gear motors provide precise control over speed and torque, enabling operators to tailor motion profiles to specific requirements and ensure consistent performance.
Reliability: With fewer moving parts and sealed enclosures to protect against dust and moisture, gear motors exhibit robustness and reliability, requiring minimal maintenance over their operational lifespan.
Versatility: The ability to select from a wide range of gear ratios makes electric gear motors adaptable to diverse applications, accommodating varying speed and torque requirements.


 English
English 中文简体
中文简体








.jpg?imageView2/2/format/jp2)